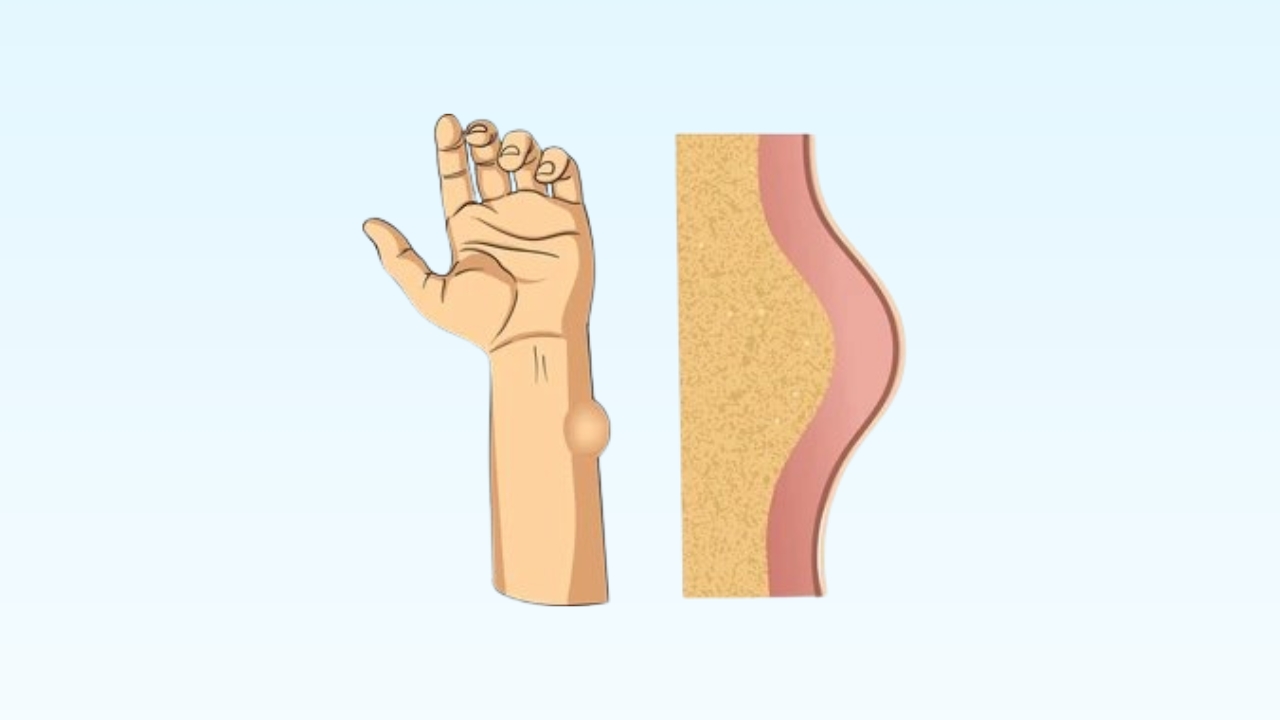
A lipoma is a slow-growing, soft lump made of fatty tissue. It usually develops just under the skin, between the skin and muscle layer. Lipomas are commonly found on areas like the neck, forehead, arms, shoulders, back, thighs, legs, and buttocks.
These lumps are generally small, round or oval in shape, painless, and move easily when pressed with fingers. Lipomas do not spread to nearby tissues and are usually harmless. Although they are called tumors, lipomas are benign (non-cancerous).
Most lipomas do not need treatment unless they cause pain, discomfort, or cosmetic concerns.
What Causes Lipoma?
The exact cause of lipoma is not clearly known. However, genetics plays an important role. If someone in your family has a lipoma, you may also develop one.
Lipomas can sometimes appear after an injury or trauma to a particular area of the body.
Certain medical conditions can also increase the risk of developing lipomas, such as:
- Gardner Syndrome – A rare condition associated with soft tissue growths, bone tumors, and intestinal polyps.
- Dercum’s Disease (Adiposis Dolorosa) – Causes multiple painful lipomas, mainly on the arms, legs, and trunk.
- Madelung’s Disease – Leads to abnormal fat buildup around the neck, shoulders, hips, and thighs.
- Familial Multiple Lipomatosis – An inherited condition causing multiple fatty lumps on the body.
- Cowden Syndrome – A genetic disorder linked with multiple non-cancerous growths, including lipomas.
Types of Lipoma
Lipomas can be located just under the skin or deep inside muscle layers. Based on their structure and content, lipomas are classified into different types.
Based on Location
- Superficial Subcutaneous Lipoma – Found just below the skin.
- Chondroid Lipoma – Deep-seated, firm lipomas that usually appear yellowish and are more common in women.
Based on Tissue Content
- Conventional Lipoma – The most common type, made only of fat cells.
- Angiolipoma – Contains blood vessels and fat; often painful.
- Fibrolipoma – Made of fat and fibrous tissue; feels firm.
- Hibernoma – Contains brown fat instead of regular white fat.
- Myelolipoma – Contains fat and blood-forming tissue similar to bone marrow.
- Spindle Cell Lipoma – Has long, spindle-shaped fat cells.
- Pleomorphic Lipoma – Fat cells of different shapes and sizes.
- Atypical Lipoma – Deeper lipomas with increased cell numbers.
How is a Lipoma Diagnosed?
Lipomas are usually diagnosed through a physical examination by a doctor. Since they grow slowly and are painless, most lipomas are harmless.
However, regular monitoring is important to check:
- Increase in size
- Pain or discomfort
- Changes in texture
These checks help rule out rare chances of cancerous changes.
When is Lipoma Removal Needed?
Lipoma removal may be advised if:
- The lump looks unpleasant or affects appearance
- It causes pain by pressing on nerves or blood vessels
- There are multiple lipomas affecting daily life
- It grows internally and causes complications (like abdominal pain or constipation)
Treatment Options for Lipoma at Medisure Surgery Care
1. Surgical Excision (Most Effective Treatment)
Surgical removal is a simple and safe outpatient procedure. Procedure includes:
- Cleaning the area and giving local anesthesia
- Making a small incision near the lipoma
- Removing the lipoma completely as a single lump
- Small cuts may not need stitches
- Larger cuts may require stitches, removed after 7–10 days
This method ensures complete removal with very low chances of recurrence.
2. Steroid Injections
- Suitable for small lipomas
- Steroids are injected to shrink the fatty tissue
- Less effective compared to surgery
- Does not remove the lipoma completely
Takeaway
Most people live with lipomas without any problem. Lipomas are painless, harmless fatty lumps and usually do not require treatment. Removal is only needed if they cause pain, discomfort, or cosmetic concerns.
Lipomas rarely return after surgery, though a new lipoma may appear in a different area. Regular monitoring is important to notice any unusual changes.
Get Expert Care at Medisure Surgery Care
If you notice any unusual lump on your body, do not ignore it. At Medisure Surgery Care, we connect you with experienced doctors and trusted hospitals for safe and effective lipoma treatment.
📞 Book a consultation with Medisure Surgery Care today and get expert advice for lipoma diagnosis and treatment.